 -->
-->Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016
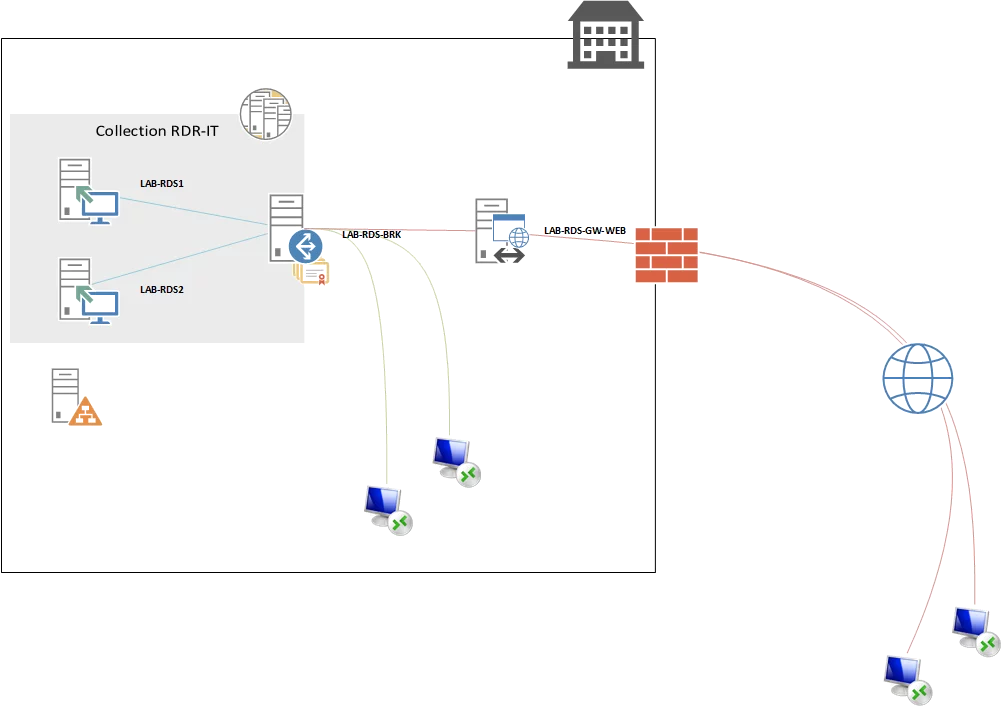
Oct 07, 2020 The Remote Desktop Gateway RDG role enables you to access your RDS environment remotely over 443. RDS Architecture. VBoring Blog Series: Setup Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2012 R2. Nov 19, 2015 Setup RD Licensing Role on Windows Server 2012 R2; Setup RD Gateway Role on Windows Server 2012 R2; RDS Architecture. Server Roles in RDS: There are three core roles to setup a RDS environment and are as follows: Remote Desktop Session Host RDSH: Applications are installed and published from the Session Host servers. Remote Desktop Connection. In this video demonstration we will see how to enable remote desktop feature (RDP) in Windows Server 2012 R2, as well as we will see how to connect Windows S.
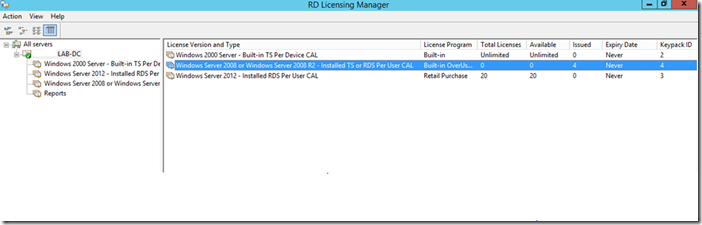
Each user and device that connects to a Remote Desktop Session host needs a client access license (CAL). You use RD Licensing to install, issue, and track RDS CALs.
When a user or a device connects to an RD Session Host server, the RD Session Host server determines if an RDS CAL is needed. The RD Session Host server then requests an RDS CAL from the Remote Desktop license server. If an appropriate RDS CAL is available from a license server, the RDS CAL is issued to the client, and the client is able to connect to the RD Session Host server and from there to the desktop or apps they're trying to use.
There is a licensing grace period of 120 Days during which no license server is required. Once the grace period ends, clients must have a valid RDS CAL issued by a license server before they can log on to an RD Session Host server.

Use the following information to learn about how client access licensing works in Remote Desktop Services and to deploy and manage your licenses:
- License your RDS deployment with client access licenses (CALs)
Understanding the RDS CAL model
There are two types of RDS CALs:
- RDS Per Device CALs
- RDS Per User CALs
The following table outlines the differences between the two types of CALs:
| Per Device | Per User |
|---|---|
| RDS CALs are physically assigned to each device. | RDS CALs are assigned to a user in Active Directory. |
| RDS CALs are tracked by the license server. | RDS CALs are tracked by the license server. |
| RDS CALs can be tracked regardless of Active Directory membership. | RDS CALs cannot be tracked within a workgroup. |
| You can revoke up to 20% of RDS CALs. | You cannot revoke any RDS CALs. |
| Temporary RDS CALs are valid for 52–89 days. | Temporary RDS CALs are not available. |
| RDS CALs cannot be overallocated. | RDS CALs can be overallocated (in breach of the Remote Desktop licensing agreement). |
When you use the Per Device model, a temporary license is issued the first time a device connects to the RD Session Host. The second time that device connects, as long as the license server is activated and there are available RDS CALs, the license server issues a permanent RDS Per Device CAL.
When you use the Per User model, licensing is not enforced and each user is granted a license to connect to an RD Session Host from any number of devices. The license server issues licenses from the available RDS CAL pool or the Over-Used RDS CAL pool. It's your responsibility to ensure that all of your users have a valid license and zero Over-Used CALs—otherwise, you're in violation of the Remote Desktop Services license terms.
An example of where one would use the Per Device model would be in an environment where there are two or more shifts using the same computers to access the RD Session Host(s). The Per User model would be best for environments where users have their own dedicated Windows device to access the RD Session Host(s).
To ensure you are in compliance with the Remote Desktop Services license terms, track the number of RDS Per User CALs used in your organization and be sure to have enough RDS Per User CALs installed on the license server for all of your users.
You can use the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager to track and generate reports on RDS Per User CALs.
RDS CAL version compatibility
The RDS CAL for your users or devices must be compatible with the version of Windows Server that the user or device is connecting to. You can't use RDS CALs for earlier versions to access later versions of Windows Server, but you can use later versions of RDS CALs to access earlier versions of Windows Server. For example, an RDS 2016 CAL or higher is required to connect to a Windows Server 2016 RD Session Host, while an RDS 2012 CAL or higher is required to connect to a Windows Server 2012 R2 RD Session Host.
The following table shows which RDS CAL and RD Session Host versions are compatible with each other.
| RDS 2008 R2 and earlier CAL | RDS 2012 CAL | RDS 2016 CAL | RDS 2019 CAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008, 2008 R2 session host | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2012 session host | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2012 R2 session host | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2016 session host | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2019 session host | No | No | No | Yes |
You must install your RDS CAL on a compatible RD license server. Any RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of Remote Desktop Services and the current version of Remote Desktop Services. For example, a Windows Server 2016 RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of RDS, while a Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS license server can only host licenses up to Windows Server 2012 R2.
The following table shows which RDS CAL and license server versions are compatible with each other.
| RDS 2008 R2 and earlier CAL | RDS 2012 CAL | RDS 2016 CAL | RDS 2019 CAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008, 2008 R2 license server | Yes | No | No | No |
| 2012 license server | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 2012 R2 license server | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 2016 license server | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2019 license server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Applies To: Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Remote Desktop Services accelerates and extends desktop and application deployments to any device, improving remote worker efficiency, while helping to keep critical intellectual property secure and simplify regulatory compliance. Remote Desktop Services enables virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), session-based desktops, and applications, allowing users to work anywhere.
Did you mean…
Did you know that Microsoft Azure provides similar functionality in the cloud? Learn more about Microsoft Azure virtualization solutions. Create a hybrid virtualization solution in Microsoft Azure: |
Role description
The Remote Desktop Services role provides technologies that enable users to connect to virtual desktops, RemoteApp programs, and session-based desktops. With Remote Desktop Services, users can access remote connections from within a corporate network or from the Internet.
Practical applications
Remote Desktop Services allows workers to work anywhere. Some of the key benefits of Remote Desktop Services include:
Unified administration experience – Administer your session and virtual desktop collections, configure your RemoteApp programs, manage your virtual desktops, and add servers to the deployment from one centralized console.
User personalization – User profile disks allow you to preserve user personalization settings across session collections and pooled virtual desktop collections.
Less expensive storage – Pooled virtual desktops can use local storage live migration between host computers. Personal virtual desktops can use storage located on network shares.
Automated pooled virtual desktop management – Deploy and manage pooled virtual desktops centrally by using a virtual desktop template. Any changes, such as application installation or security updates, are installed on the virtual desktop template, and the pooled virtual desktops are then recreated from the virtual desktop template.
New and changed functionality for Windows Server 2012 R2
In Windows Server 2012 R2, Remote Desktop Services includes enhancements in the following areas:
Monitor and control by using session shadowing
Reduced storage requirements and improved performance accessing common data
RemoteApp programs perform more like locally-based applications
Improved reconnection performance for remote clients
Improved compression allowing improved usage of network bandwidth
Display resolution changes are automatically reflected on the remote client
RemoteFX virtualized GPU supports DX11.1
For more information about new features and functionality, see What's New in Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server.
New and changed functionality for Windows Server 2012
Remote Desktop Services enables the mobile work force to connect to desktop and applications from anywhere. In Windows Server 2012, Remote Desktop Services includes enhancements in the following areas:
Simplified Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) deployment and management
Simplified Session Virtualization deployment and management
Centralized resource publishing
Rich user experience with Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
The user experience has been enhanced for Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2012 in the following ways:
Rich Windows desktop remoting experience
Smooth audio and video playback experience
Rich graphics and video user experience over a WAN
Enhanced device remoting support with USB Redirection for Session Virtualization and VDI
True Multi-Touch and gesture remoting
Email name discovery and subscription to administrator supplied remote resources
RemoteFX virtualized GPU provides DX 11 support
In addition to these areas of enhancement, Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2012 introduces a new management console for managing the majority of Remote Desktop Services-related tasks. For more information about new features and functionality, see What's New in Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server.
New Microsoft Remote Desktop Clients
You can use the Microsoft Remote Desktop client to connect to a remote PC and your work resources from almost anywhere. Experience rich interactivity using a remote desktop client designed to help you get your work done wherever you are. For example, you can connect to your work PC and have access to all of your apps, files, and network resources as if you were sitting right in front of your work PC. You can leave apps open at work and then see those same apps using the RD client.
For information about these new features and functionality for Android, iOS, and Mac, see Microsoft Remote Desktop Clients.
Removed or deprecated functionality
For a list of deprecated features, see Features Removed or Deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Features Removed or Deprecated in Windows Server 2012.
Hardware requirements
Remote Desktop Services requires that the Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 operating system be installed. There are no additional hardware or software requirements for running Remote Desktop Services.
There are several hardware requirements that must be met when you deploy RemoteFX virtualized GPU to hardware accelerate your Windows client virtual desktops:
SLAT-enabled processor. The processor on the RemoteFX server must support Second-Level Address Translation (SLAT).
GPU. At least one graphics processing unit (GPU) that is capable of supporting RemoteFX is required on the RemoteFX server. The GPU driver must support DirectX 11.
Note
Without a RemoteFX virtualized GPU, applications that require DirectX will still work using a built in Hyper-V specific GPU.

Installing Remote Desktop Services 2012 R2
Server Manager information
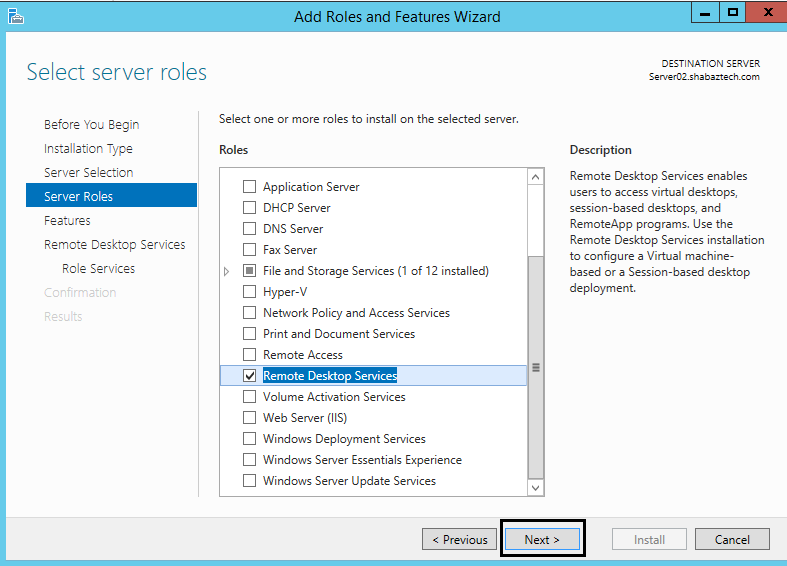
Remote Desktop Services is a server role that consists of several role services. In Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012, the following Remote Desktop Services role services can be installed with this role:
Role service name | Role service description |
|---|---|
RD Virtualization Host | Remote Desktop Virtualization Host (RD Virtualization Host) integrates with Hyper-V to deploy pooled or personal virtual desktop collections within your organization. |
RD Session Host | Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) enables a server to host RemoteApp programs or session-based desktops. Users can connect to RD Session Host servers in a session collection to run programs, save files, and use resources on those servers. |
RD Connection Broker | Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RD Connection Broker):
|
RD Web Access | Remote Desktop Web Access (RD Web Access) enables users to access RemoteApp and Desktop Connection through the Start menu on a computer that is running Windows 8, Windows 7, or through a web browser. RemoteApp and Desktop Connection provides a customized view of RemoteApp programs and session-based desktops in a session collection, and RemoteApp programs and virtual desktops in a virtual desktop collection. |
RD Licensing | Remote Desktop Licensing (RD Licensing) manages the licenses required to connect to a Remote Desktop Session Host server or a virtual desktop. You can use RD Licensing to install, issue, and track the availability of licenses. |
RD Gateway | Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) enables authorized users to connect to virtual desktops, RemoteApp programs, and session-based desktops on an internal corporate network from any Internet-connected device. |
See also
The following table provides additional resources for evaluating Remote Desktop Services.
Install Remote Desktop Server 2012
Content type | References |
|---|---|
Product evaluation | |
Community resources | |
Related technologies |
