Must know These Before taking Covishield Vaccine should be known in hand. It’s time to get secure from the corona.
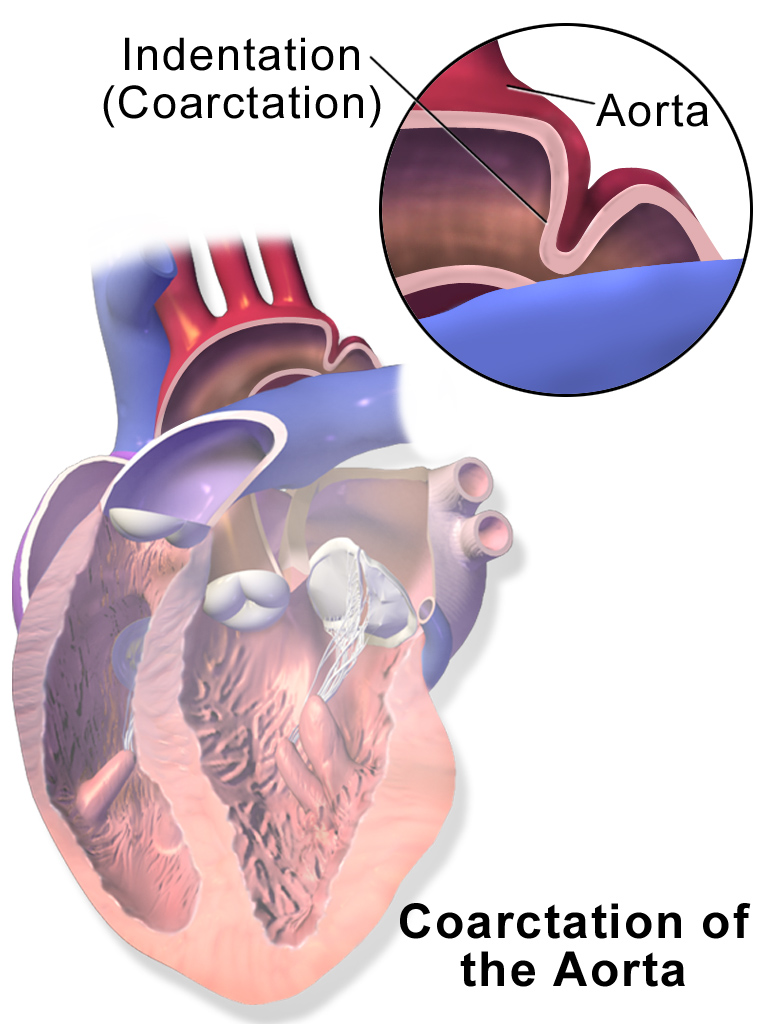
Simultaneous palpation of two pulses can be diagnostic in radiofemoral delay. Normally the femoral and the radial pulses occur simultaneously.When the femoral pulse lags behind the radial (radio-femoral delay), occlusion of the aorta either due to coarctation or atherosclerosis is diagnosed. Reduced amplitude and delayed timing of the pulses in the lower body compared to the pulses in the upper body. I was diagnosed with radiofemoral delay by a cardiologist (saw for chest pains), but my CT aortagram was normal. This was a year back now, but it’s been playing on my mind, especially given that I’ve been having these chest pains again recently (in fact they feel a.
Covishield is the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine which is locally manufactured by the Serum Institute of India. Serum institute India is the world’s largest vaccine manufacturer.

It had already said that it is producing more than 50 million Covishield vaccine doses a month.
The Covishield™ by AstraZeneca is already used in clinical trials where the participants received one or two doses in overseas and Indian trials.
These Clinical trials are a three-phased process to determine whether the vaccine induces good immune responses and whether it causes any unacceptable side-effects.
What is Covishield?
Covishield vaccine is made from a weakened version of a common cold virus also known as an adenovirus from chimpanzees. It has been modified in the lab to look more like coronavirus – although it can’t cause illness.
The Vaccine making company, Serum Institute (SII), says that it is highly effective and backed by phase III trial data from Brazil and United Kingdom.
how does Covishield work?
When the vaccine is injected into the person, it activates the immune system of the person’s body. Then our bodies start to make antibodies against the virus. This antibody is targeted on the attack to any type of coronavirus infected towards our body.
Dosage of Covishield Vaccine
The covishield vaccine is administered as two doses given between four and 12 weeks apart.
When you receive one dose of the Covishield vaccine, then the second dose should be taken between 4 to 6 weeks after the first dose.
However, you can take the second dose up to 12 weeks after the first dose from according to different studies.
When you miss your second dose, you need to ask your healthcare provider for further advice on how you complete the dose.
Contents of Covishield Vaccine
The contents of the covishield vaccine contain the following contents:
- L-Histidine
- L-Histidine hydrochloride monohydrate
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
- Polysorbate 80
- Ethanol
- Sucrose
- Sodium chloride
- Disodium edetate dihydrate (EDTA)
- Water for injection.
Storing of Covishield Vaccine
This vaccine can be stored at temperatures of 2C to 8C safely. This means that it can be stored about the same as a domestic refrigerator. The easy storing makes easier to store as well as distribute in comparison to another version of vaccines by other countries.
The vaccine which is developed by Pfizer-BioNTech company must be stored below -70 degree centigrade which is a challenge for developing countries like India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Srilanka, and other
Effectiveness of Covishield?
As per the previous International clinical trials of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, it showed that the effectiveness hit 90% on its half and full dose. But as it’s new and is in the trial phase, there was not enough clear data.
However, the data shows that given the vaccine in different trials was found to be 70% effective after the first dose.
Who can take the Covishield vaccine?
Covishield vaccine has been approved for restricted use in an emergency in individuals 18 years of age and older.
Who should not take the Covishield vaccine?
The person with the following medical conditions and other conditions shouldn’t take the covishield vaccine. If you are planning to take the vaccine, then you should tell the health care provider or the person who is giving you the vaccine.
- When you have an allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) of any drug
- If you have a severe allergic reaction on the previous dose of the COVID vaccine
- If you are allergic to food or other materials
- If you get an allergy to any type of vaccine or any
- If you are allergic to the contents and ingredients of the COVISHIELD™ vaccine
- If you have a fever
- If you have a bleeding disorder
- If you are taking blood thinner medicine like aspirin, clopet, warfarin, and so on.
- If you are immunocompromised patients
- If you are taking the medicine that affects your immune system like anti-cancer drugs, DMRD for Rheumatic Arthritis, immune disease
- If you are pregnant else, you plan to become pregnant
- If you are a breastfeeding mother
Summary,
The corona vaccine has been made by multiple companies. Many trials have been still in progress on the effectiveness of the vaccine. The Covishield vaccine is also in trails phase and had already completed 2nd and 3rd trials with good response and effectiveness.
As the data is not so sufficient, the adverse effect following the covishield vaccination is found to be not much to be worried about. Can know more about Covishield Factsheet The preceding data will surely come into existence in the following days.
Contents to Go ThroughhideWhat is Covishield?how does Covishield work?Dosage of Covishield VaccineContents of Covishield VaccineStoring of Covishield VaccineEffectiveness of Covishield?Who can take the Covishield vaccine?Who should not take the Covishield vaccine?Related posts:Related posts:
The anatomy of (he radial, brachial and carotid pulses have been described I p. 83).
Femoral artery. The I'emoral artery is situated just below the inguinal ligament, midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis (mid-inguinal point). It is immediately lateral to the femoral vein and medial to the femoral nerve. In the obese it can be difficult to feel.
Popliteal artery. At the level of the knee crease, the artery lies deep in the popliteal fossa and the pulse is sometimes difficult to feel, even by the experienced clinician.
Examination sequence
Posterior tibial artery. This is located 2 cm below and posterior to the medial malleolus where it passes beneath the flexor retinaculum between flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus.
Dorsalis pedis artery. This is the continuation of the anterior tibial artery on the dorsum of the fool. It passes lateral the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus and is best fell at the proximal exlcnt of the groove between the first and second metatarsals. It may be absent or abnormally sited in 10% of normal subjects, sometimes being 'replaced' by a palpable perforating peroneal artery.
Individual pulses should be recorded as follows:
Radiofemoral Delay Time
normal +

reduced ± absent aneurysmal ++
Fig. 3.38 Examine the femoral artery, simultaneously while checking for radiofemoral delay.
Femoral
□ With the patient supine, firmly press down and cephalad in the groin crease (Fig. 3.38) using two or three extended fingers.
□ Auscultate for a bruit.
□ Check for radiofemoral delay.
Popliteal
□ Flex the knee to 30 degrees and make sure the patient is relaxed.
Examination of pulses
If the examiner is in any doubt aboul which pulse is beins; felt, it is useful for the clinician lo palpate his or her own pulse at the same time. Lack of synchronisation implies that it is the patient's pulse.
General
□ Examine the radial, brachial and carotid pulses (p. 83). Measure the blood pressure in both arms.
I Palpate and auscultate over the abdominal aorta in any patient with suspected vascular disease.
□ Inspect the legs and feet for changes of ischaemia including changes in temperature and colour,
□ Note any scars from previous vascular or non-vascular surgery and the position, margin, depth and colour of any ulceration.
□ Specifically look between the toes and at the heel.s lor ischaemic changes.
Fig. 3.39 Examination of the popliteal artery. Feel the popliteal artery with the fingertips, having curled both hands into the popiiteal fossa.
Fig, 3.40 Examination oi E the posterior tibial artery and IB the dorsal is pedis artery.
□ With the thumbs in front and the fingers behind, press firmly over the popliteal artery.
Feel for (he pulse in the midline 3^1 cm below the knee crease where the artery can be compressed against the posterior aspect of the tibia as il passes under the soleal arch (Fig. 3.39).
Posterior tibial
□ f-'eel 2 cm below and 2 cm behind the medial malleolus (Fig 3.40A).
Dorsalis pedis
□ Feel in the middle of the dorsum of the foot just lateral to the tendon of extensor hallucis longus (Fig. 3.40B).
□ With the patient lying supine, stand at the foot of the bed. Raise the feet and support the legs at 45 degrees to the horizontal.
Radiofemoral Delay
□ Then ask (he patient to sit up and swing the legs over the edge of the bed.
Aortic Coarctation Life Expectancy
Continue reading here: Chronic lower limb ischaemia
Was this article helpful?
